
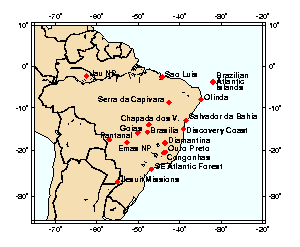

Ouro Preto is Portuguese for "Black Gold". The city grew out of a gold mining town which developed in the early 18th century. In 1711 the city was named Vila Rica, and many houses used the old entrances to mine shafts as their cellars. The prosperity of the city based on gold led to splendid architecture and some of the buildings are among the most beautiful examples of baroque art in the world.
Olinda was founded in 1535 as a local administrative capital. It prospered due to the local sugar industry, but developed slowly such that the original layout of the town is almost entirely preserved.

Located on the border between Argentina and Brazil, this is one of the most spectacular waterfalls in the world. It is 80 metres high and 2,700 metres in diameter and surrounded by sub-tropical rainforest with over 2,000 species of plants and numerous wildlife including: tapirs, giant anteaters, howling monkeys, ocelots, and jaguars.
The city was founded in 1549 as the first capital city of the Portuguese colony.
This is a religious complex with small chapels and the much larger Church of Bom Jesus de Matosinhos, built in 1757. The church is renowned for its rococo interior with 89 offerings covering the walls of "The House of Miracles".
The federal capital of Brazil is a new city of approximately 1 million people. It is notable as a planned city and considered to be a masterpiece of modern architecture and art. It was designed in 1956 by urban planner Lucio Costa and architect Oscar Niemeyer.

Serra da Capivara National Park contains numerous rock shelters decorated with cave paintings, some more than 25,000 years old.
These ruins are included as part of the Jesuit Missions of the Guaranis site found in Argentina and Brazil. Other missions include: San Ignacio Mini, Santa Ana, Nuestro Senora de Loreto and Santa Maria Mayor.
Sao Luis is an example of an Iberian colonial town.
The Brazilian Discovery Coast includes a number of areas containing the best and largest remaining examples of Atlantic forest in the northeast region of Brazil. Located in the states of Bahia and Espirito Santo.
These Atlantic Forest Reserves are in the states of Pirana and Sao Paulo.
The colonial village of Diamantina developed with the rise of diamond prospecting during the 18th century.
This is one of the world's largest freshwater wetland ecosystems. The area preserves habitats representative of the Pantanal that contain a number of globally threatened species.
Expanded from Jau National Park site.
The Negro River watershed located in the Amazonian central plain is the largest national park in the Amazon Basin. It is an example of a "blackwater ecosystem". The name is taken from the color given to the water by the decomposition of organic matter and the lack of terrestrial sediments.
The Fernando de Noronha volcanic group, located in the South Atlantic Ocean, 225 miles NE of Cabo de Sao Roque; has been strategically important for defense due to its position off bulge of Brazil.
This is one of the world's oldest and most diverse tropical ecosystems.
This visionary garden city was created in 1940 at Belo Horizonte. It was designed around an artificial lake and included a casino, a ballroom, the Golf Yacht Club and the Sao Francisco de Assis church. The buildings were designed by architect Oscar Niemeyer, in collaboration with innovative artists. The Ensemble comprises bold forms that exploit the plastic potential of concrete, while fusing architecture, landscape design, sculpture and painting into a harmonious whole.
The former harbour area of Rio de Janeiro in which the old stone wharf was built for the landing of enslaved Africans reaching the South American continent from 1811 onwards.
Paraty is one of Brazil's best preserved coastal towns. In the 17th century it was the end-point of the Caminho do Ouro (Gold Route) along which gold was shipped to Europe. The site also includes four protected natural areas of the Brazilian Atlantic Forest.
Former property of renowned landscape architect Roberto Burle Marx.
Lynn Salmon <>{
Last Updated: August 13, 2021